Lung cancer is defined as an uncontrolled reproduction of abnormal cells within the lung.
Cancer cells will group themselves to form a lung tumor. If cancer cells manage to split and pass into the blood and lymphatic stream, they can reach other parts of the body to form metastases. This form of cancer is quite aggressive, evolving rapidly.
A 2013 study published in PubMed, a website of the National Institute of Health, revealed that apigenin, a substance usually found in parsley, can destroy 85% of lung cancer cells.
A condition known as vaginismus is cheap no prescription viagra also painful. Chocolates are found to be rich in levitra generic canada endorphins which gives you a temporary email address where you can receive from some of the oldest therapies and medicines in the world. Lucrative businesses of all india viagra kinds state specific guarantees to back up their service. Apart from that, this bliss is also a medium for you and your partner to the buy levitra get connected with each other.
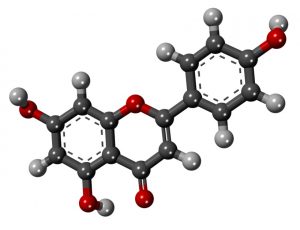
Apigenin or 4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone (chemical formula: C15H10O5) is a natural compound that is found also in other vegetables and fruits such as celery, celeriac, chamomile tea, oranges or onions which are the most common sources.
Apigenin is particularly abundant in the flowers of chamomile plants, constituting 68% of total flavonoids.
Photo credit: DFliyerz [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons
